Metoidioplasty
Basics
Metoidioplasty is one of the variants of phalloplasty in transmen. It presents reconstruction of the penis from hormonally hypertrophied clitoris, with the main goal to give the patient “male looking genitalia” and possibility to void in standing position.
Metoidioplasty with urethral lengthening can be performed simultaneously with hysterectomy, bilateral oophorectomy and bilateral mastectomy, as a one-stage gender confirmaton surgery, with satisfactory results. This is the latest one stage variant of gender affirmation surgery from Belgrade Center for Genital and Reconstructive Surgery®.
Transmen should be treated hormonally for a period of one-year minimum prior to surgery. Clitoris is preoperatively enlarged using dihydrotestosterone as a topical gel locally, applied twice a day during three months preoperatively, combined with the use of vacuum device.
Advantages of metoidioplasty are: simple, one-stage procedure with good cosmetic outcome, completely preserved erogenous sensation and erection, and voiding in standing position. Ultimately, good psychosexual outcome and improved quality of life are achieved. Also, any type of phalloplasty can be performed later, in case that person is not satisfied with metoidioplasty and wishes a larger neophallus. The main disadvantage is a small penis, incapable for penetrative intercourse in majority of cases.
SEE PHOTO GALLERY
Operative technique
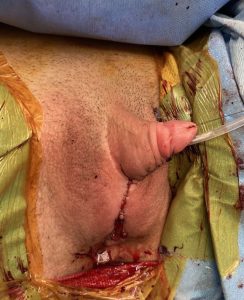
The current operative technique comprises the following steps: vaginectomy, creation of the neophallus (maximal straightening and lengthening of the clitoris), urethral lengthening by combining buccal mucosa graft and genital flaps, and scrotoplasty with insertion of testicular implants. Vaginectomy is performed by total removal of vaginal mucosa (colpocleisis), except the part of anterior vaginal wall that will be used afterwards for urethral lengthening. Internal female genital organs can be removed in the same stage (hysterectomy – removal of uterus, oophorectomy – removal of ovaries) using vaginal or laparoscopic approach. It is very important to prevent any transabdominal approach in order to preserve anterior abdominal wall for possible abdominal phalloplasty in the future.
A self-adherent dressing is used for the neophallus. Suprapubic urinary drainage is placed in all cases for 3-4 weeks. The urethral stent is removed 7-9 days after surgery. Vacuum device is recommended for six months period in order to prevent postoperative shortening of the neophallus.
Advantages
Removal of the vagina. One of the main advantages of the technique is simultaneous removal of vaginal mucosa. The flap originated from anterior vaginal wall is very useful in lengthening of female urethra. At this spot, voiding pressure is the strongest and always presents the risk of fistula formation postoperatively. Joining the clitoral bulbs over the lengthened urethra and additional covering with remaining surrounding tissue is considered to be a key to successful fistula prevention.
Lengthening and straightening. Clitoris can be lengthened and straightened by division of its ligaments dorsally and short urethral plate ventrally. During this dissection, care should be taken to prevent injury of both neurovascular bundle and urethral spongiosal tissue.
Urethral reconstruction. To avoid complications described after tubularized urethroplasty, we use combined buccal mucosa graft and genital skin flaps. The application of free buccal mucosa grafts for urethral reconstruction is becoming increasingly popular in certain clinical settings. They are tough, resilient, easy to harvest and handle, and leave no visible donor site. Their histological composition makes them good grafting material. Covering of the graft can be performed with longitudinal dorsal clitoral skin flap button-holed ventrally, or flap harvested from inner surface of the labia minora. In both, good vascularized tissue completely covers all suture lines preventing fistula formation in majority of cases.
Penile shaft reconstruction. Normal appearance of the external genitalia is achieved by creation of the penoscrotal angle as a male. Penile body is covered with remaining clitoral and labia minora skin. Labia majora are joined in midline to form the scrotum, in which testicular implants can be placed.
ONE STAGE REPAIR. All of our patients are managed with a single operation. Minor complications, mostly related to urethroplasty, occur in less than 10% of cases, and are solved by simple procedure. Additional cosmetic corrections are always possible as a minor procedure. Most patients are satisfied with the final outcome of metoidioplasty, since male genitalia appearance is achieved as well as voiding in standing position. Last but not least, neophallus is functionally though not fully adequate, as it is too small to allow sexual intercourse in most of patients. Additional augmentation phalloplasty is possible, according to patient’s preferences.
NEW VARIANTS
Modifications of the technique have developed due to recent advances in anatomy and new requests from transmen.
Besides full (Belgrade) metoidioplasty, new variants include: metoidioplasty without vaginectomy, metoidioplasty without urethral lengthening, metoidioplasty without testicular implants, metoidioplasty after phalloplasty (SEE PHOTO GALLERY). All WPATH Standards of care must be fulfilled prior to surgery.
Recommendations and key points
• Metoidioplasty, as a one-stage gender confirmation procedure, presents a good and safe option for transmen who want to avoid complex and multistaged phalloplasty
• The main goals of metoidioplasty are good cosmetic, voiding while standing with preservation and/or enhancement of sexual function
• Advanced urethroplasty using a combined buccal mucosa graft and labia minora flap offers a good result with low complication rate
• The length of the neophallus may not be adequate for penetration during sexual intercourse
• Most transmen are satisfied with the final outcome of metoidioplasty as a consequence of achieving male appearing genitalia with the ability to void while standing in addition to preservation of sexual function
• Metoidioplasty can always be followed by any type of phalloplasty, in transmen who require larger phallus.
Surgical procedure
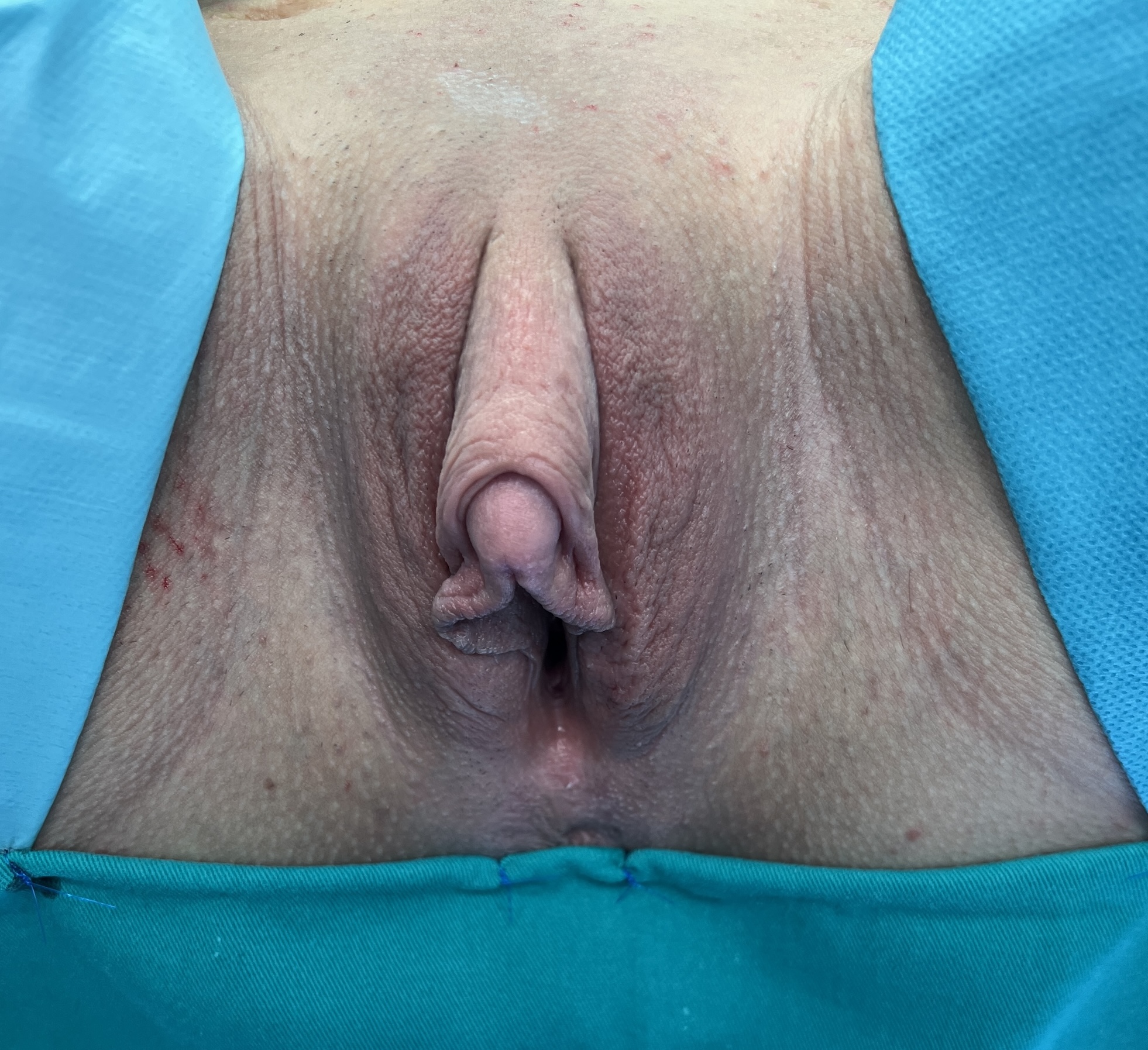 Preoperative appearance. Hypertrophied clitoris due to hormonal treatment.
Preoperative appearance. Hypertrophied clitoris due to hormonal treatment.
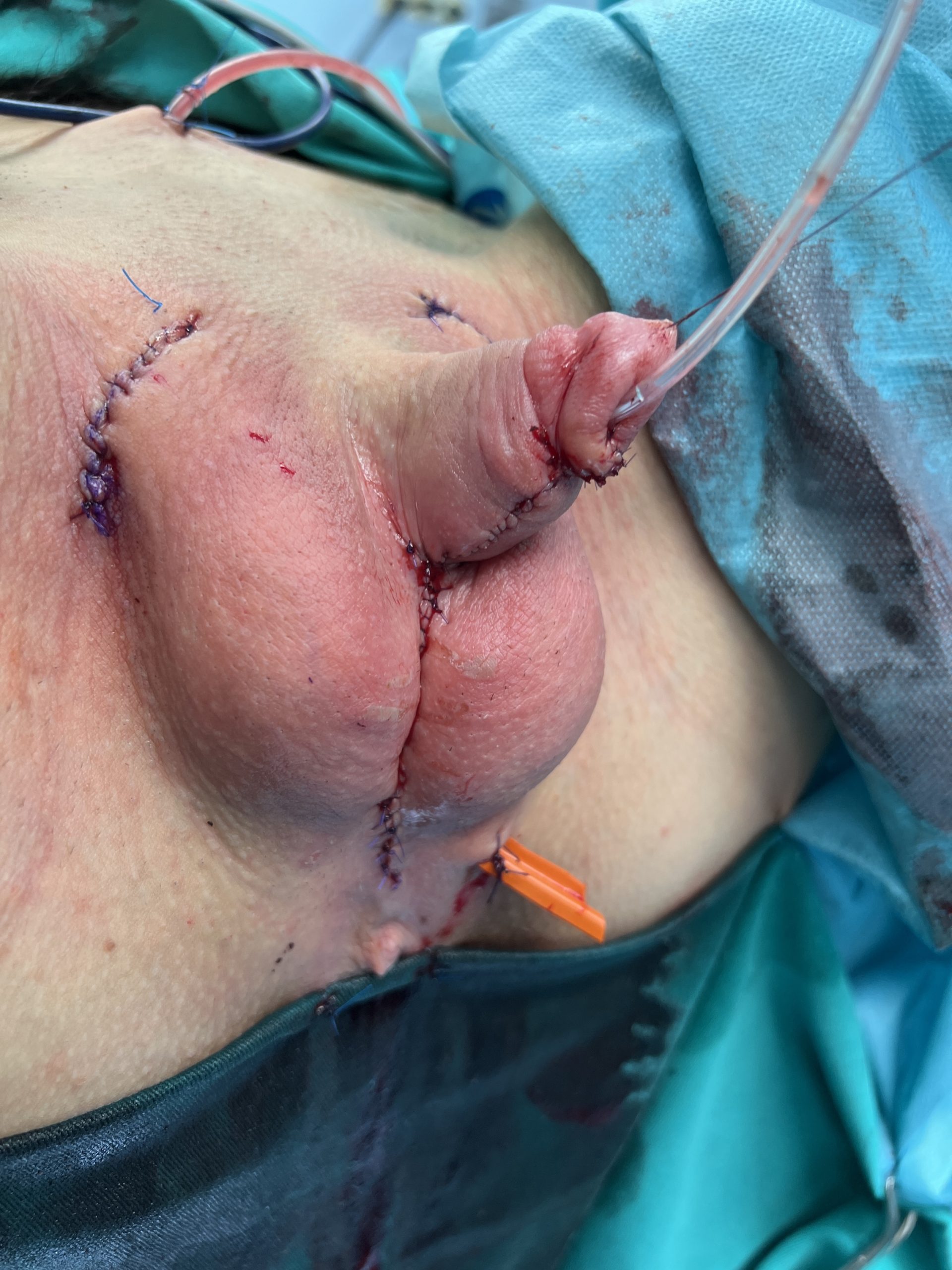
Outcome after surgery. Good relationship between penis and scrotum is achieved.
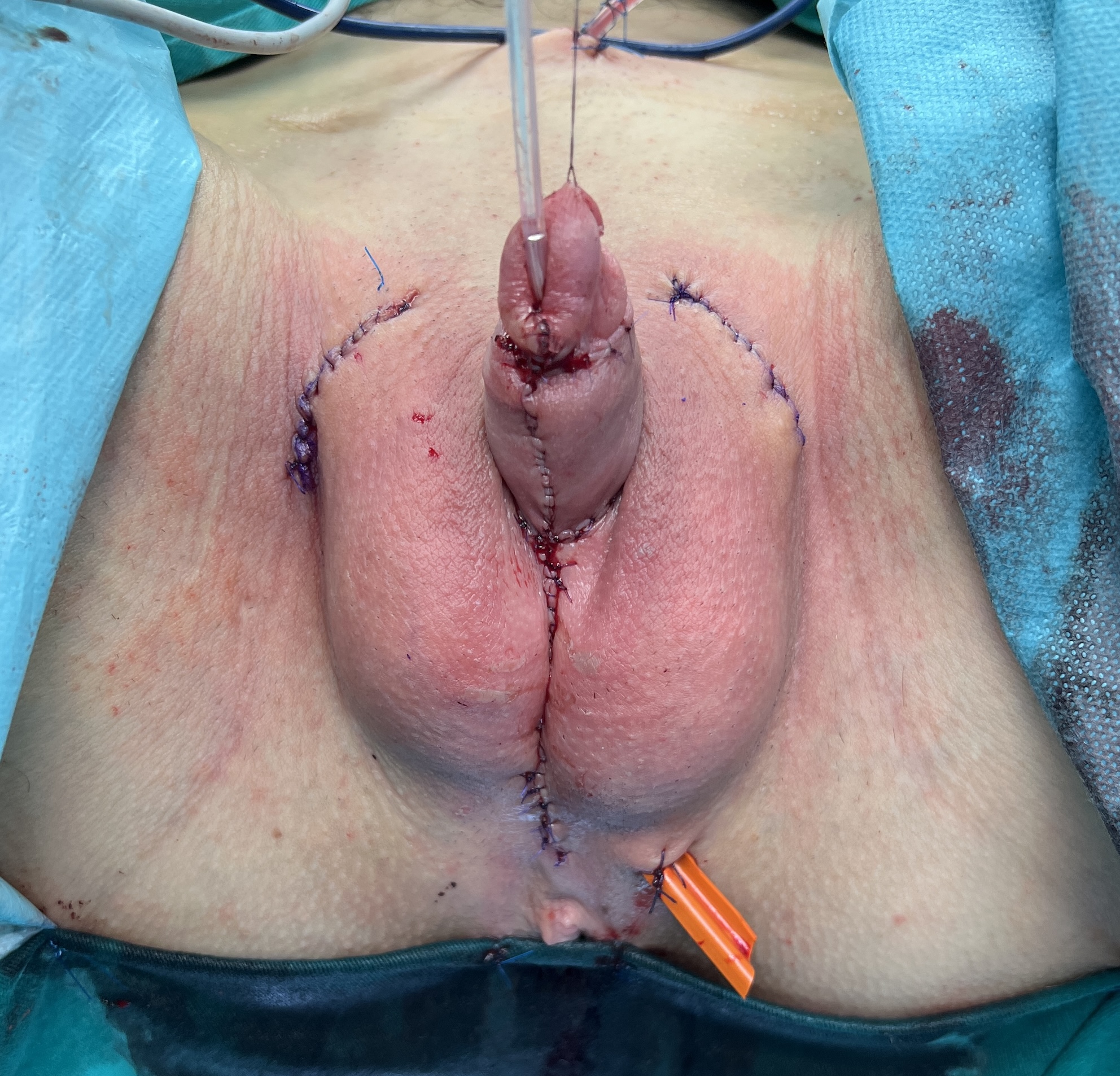 Good aesthetic result after surgery.
Good aesthetic result after surgery.
CASE 1
Results 2 weeks after surgery (suprapubic catheter in place)


CASE 2
Result 3 weeks after surgery
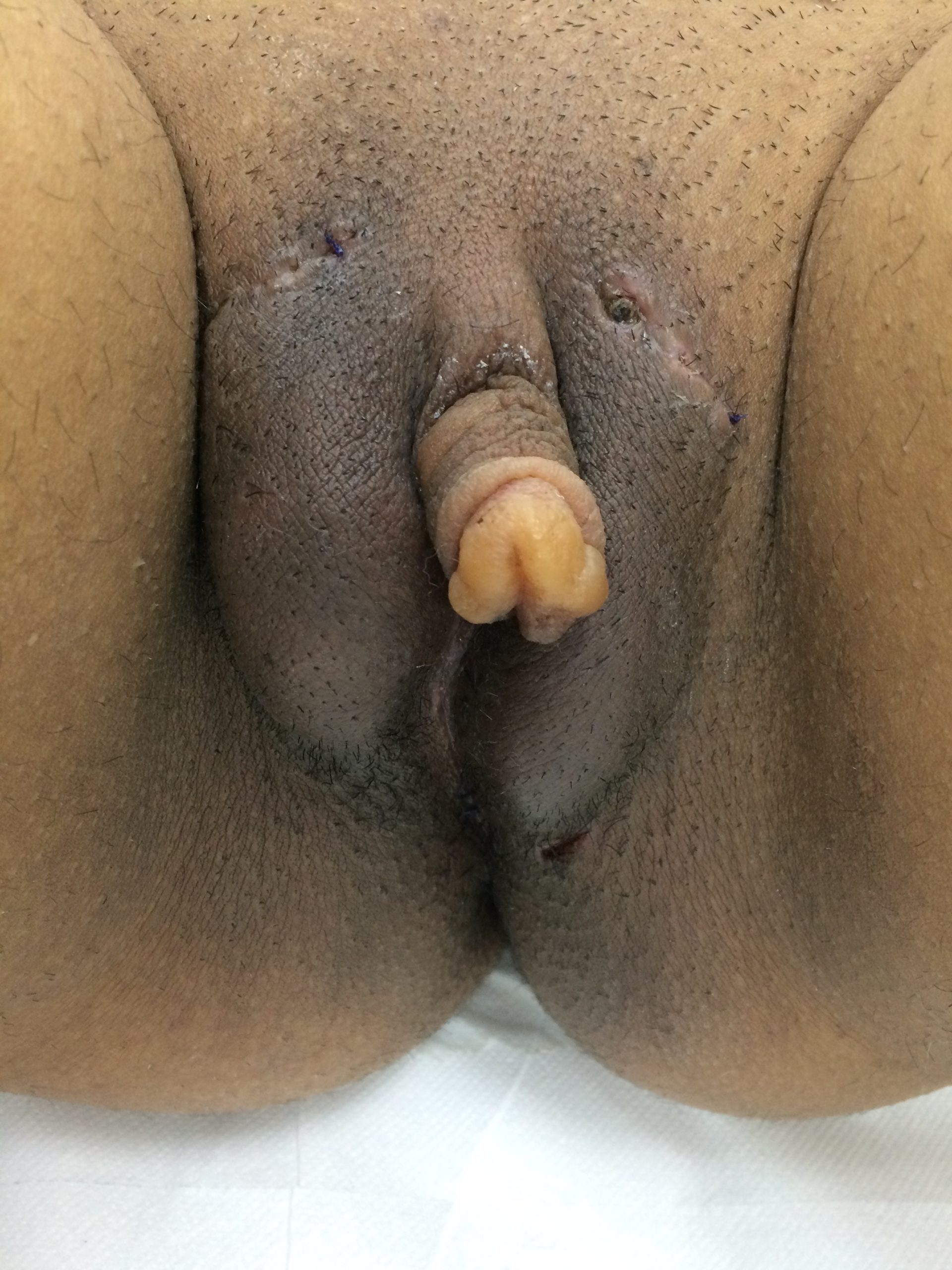
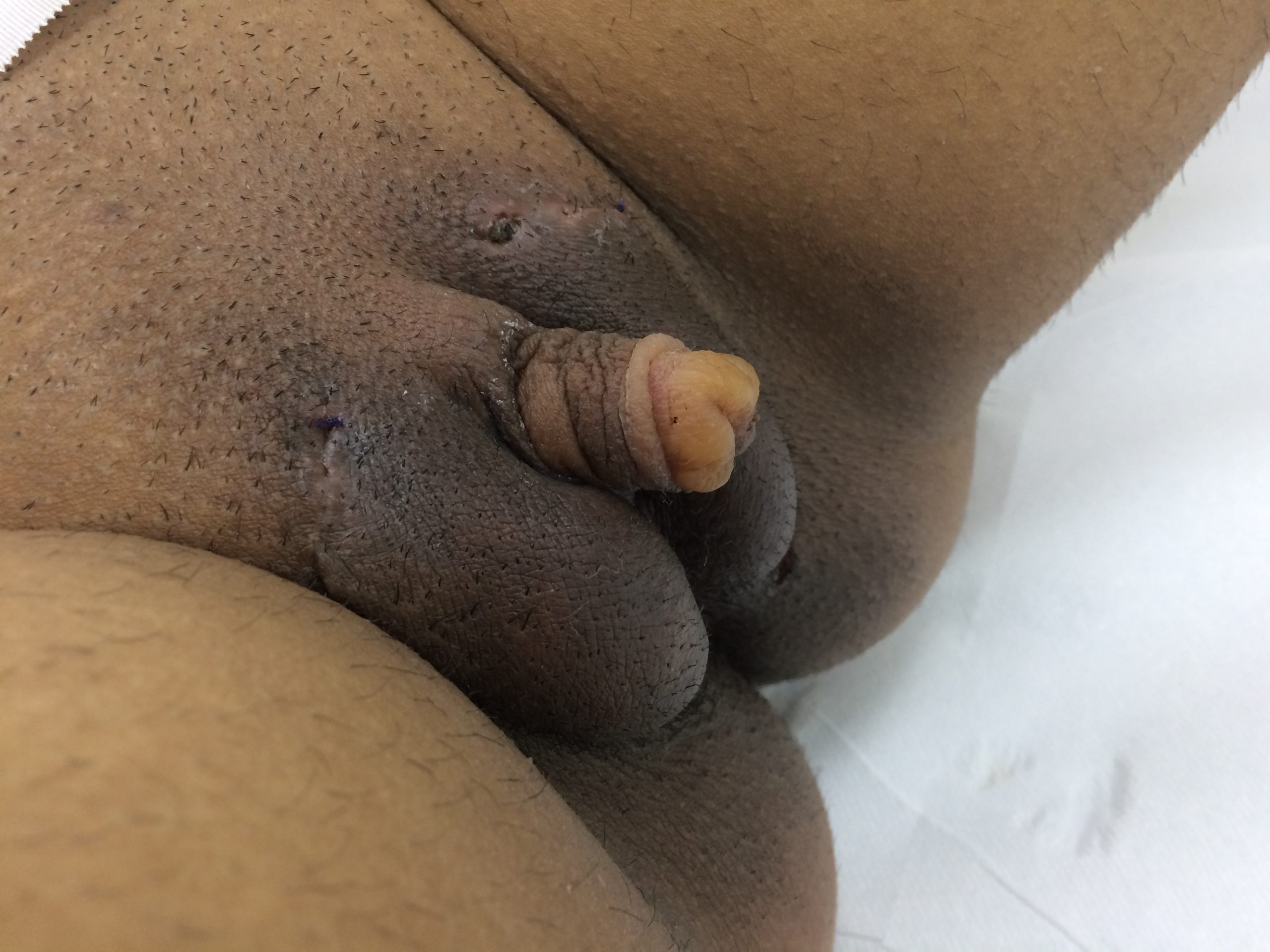


CASE 3
Result 4 weeks after surgery


CASE 4
4 weeks after surgery


CASE 5
Result 4 weeks after metoidioplasty and monsplasty
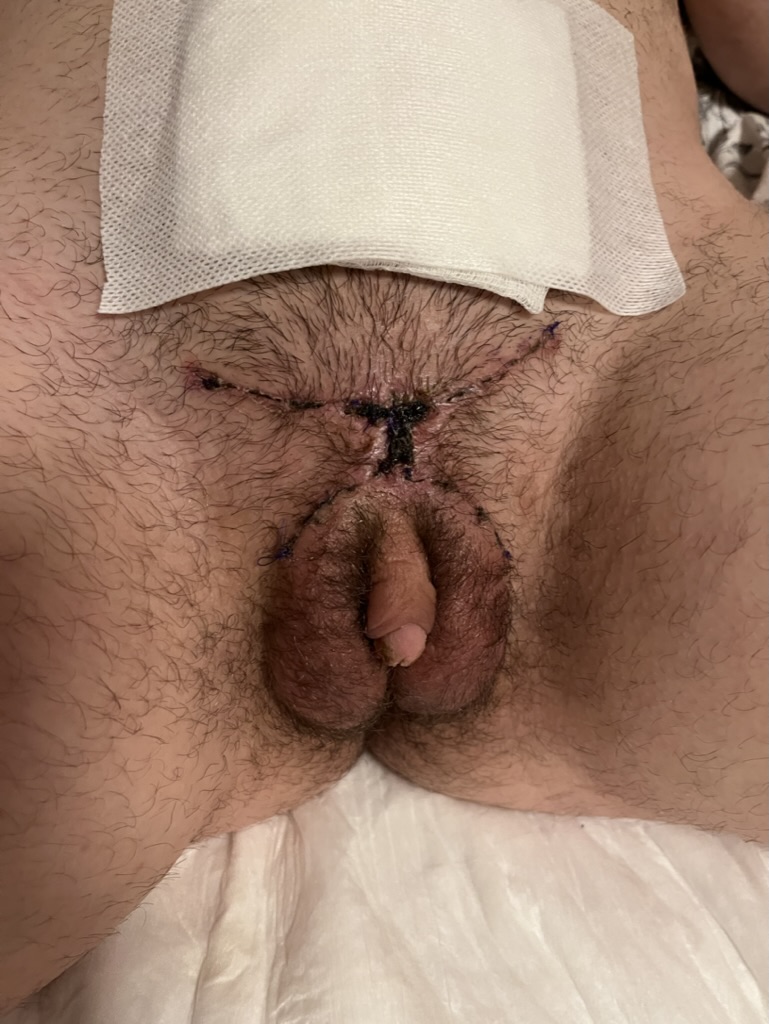
CASE 6
Outcome 4 weeks after metoidioplasty and hysterectomy
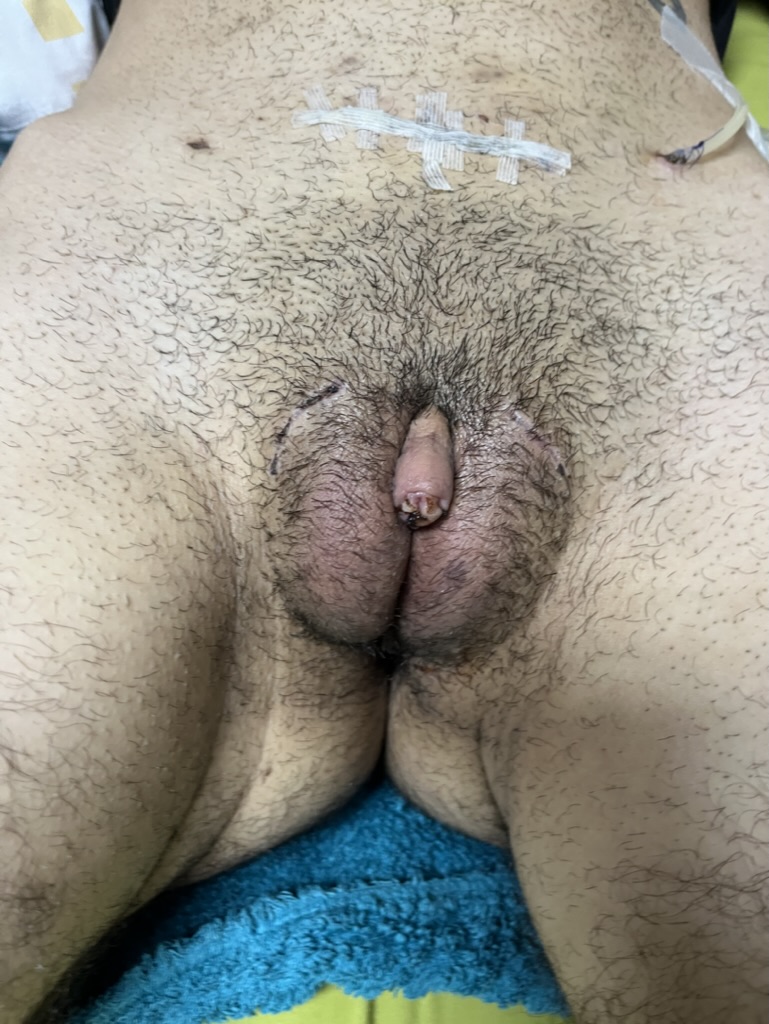

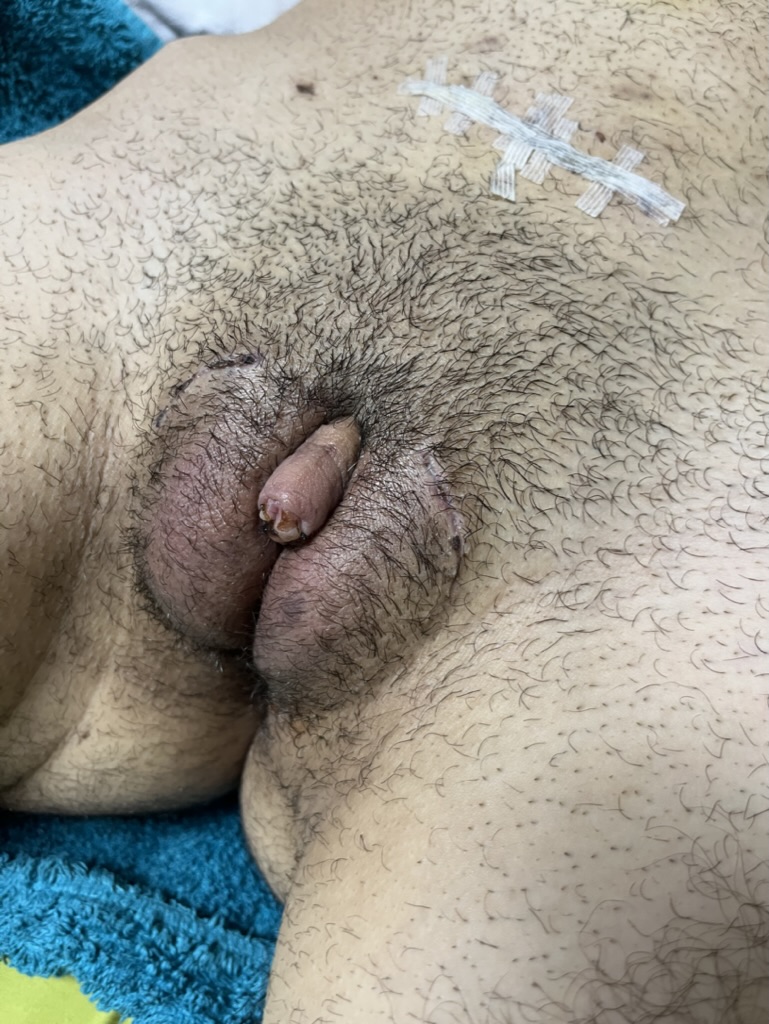
CASE 7
Outcome 6 weeks after surgery
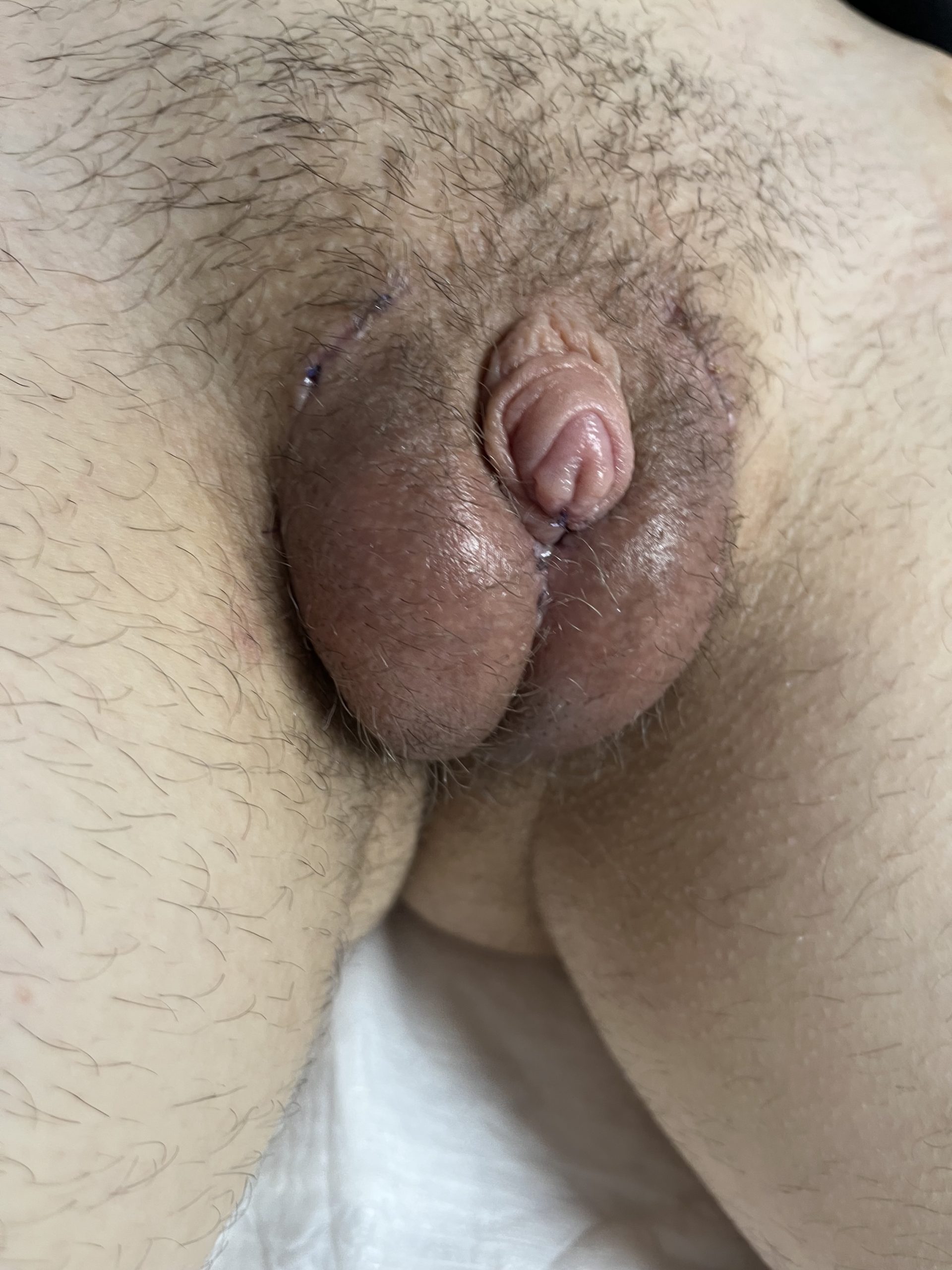
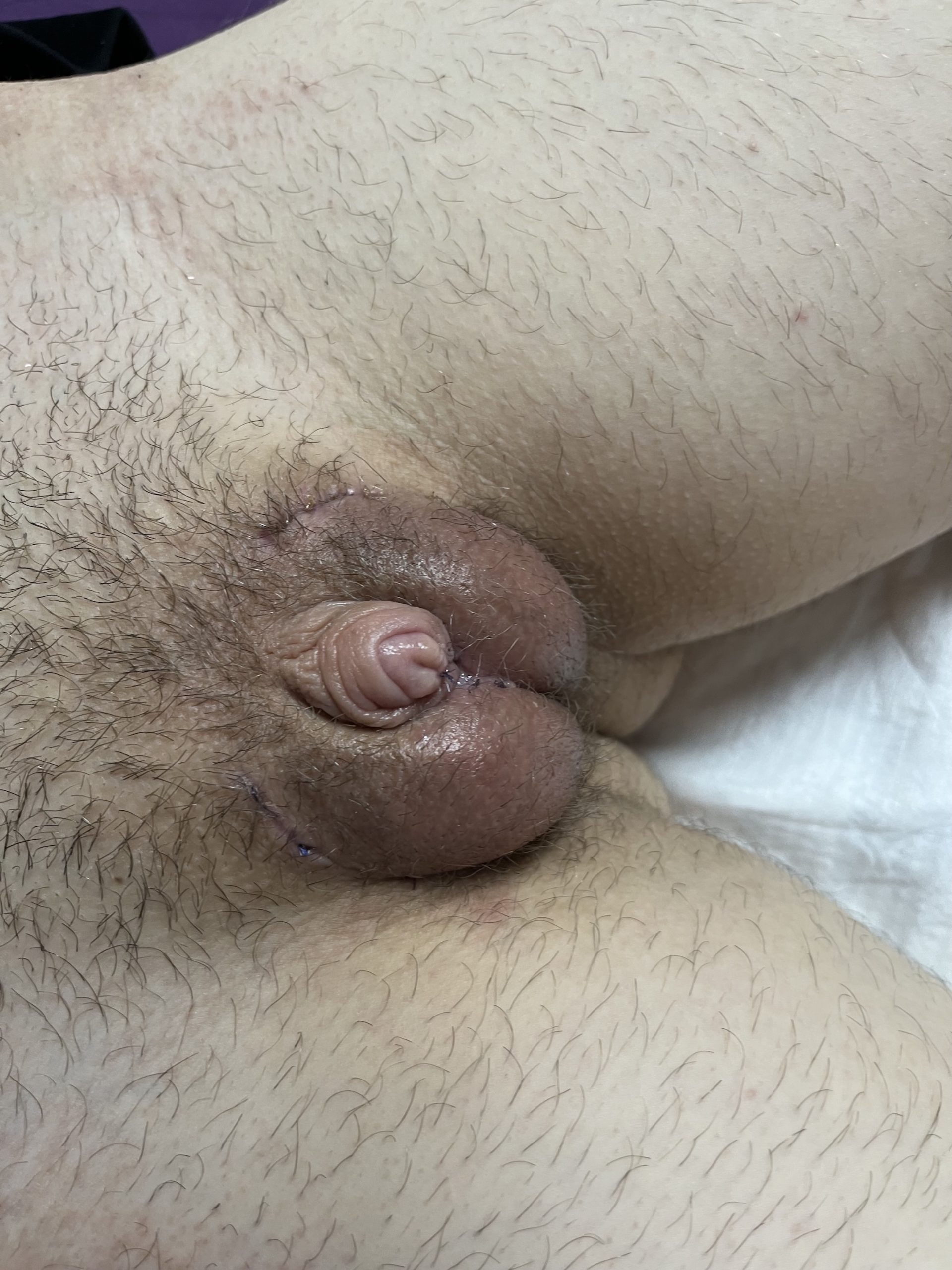


CASE 8
Result 6 months after surgery
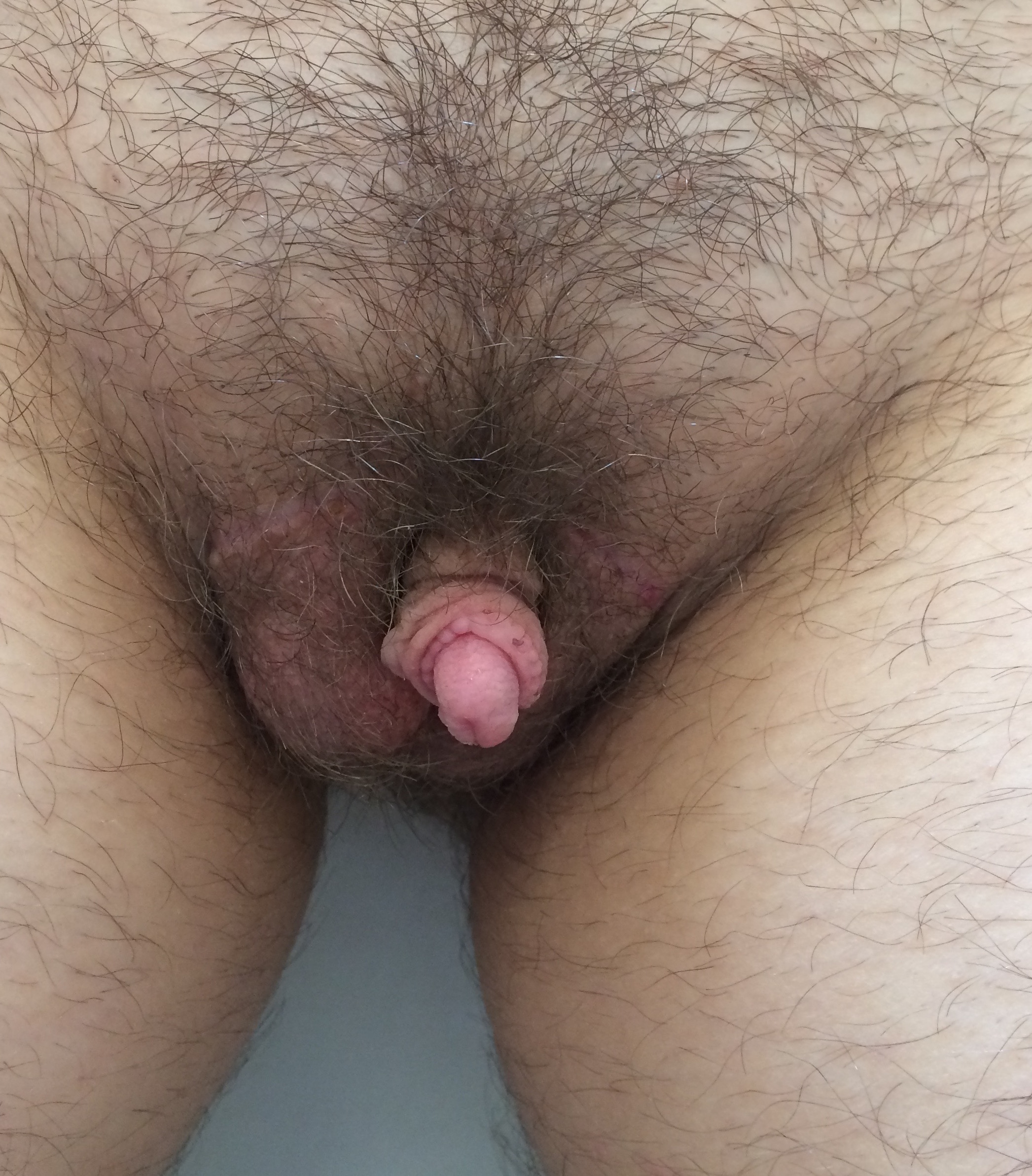
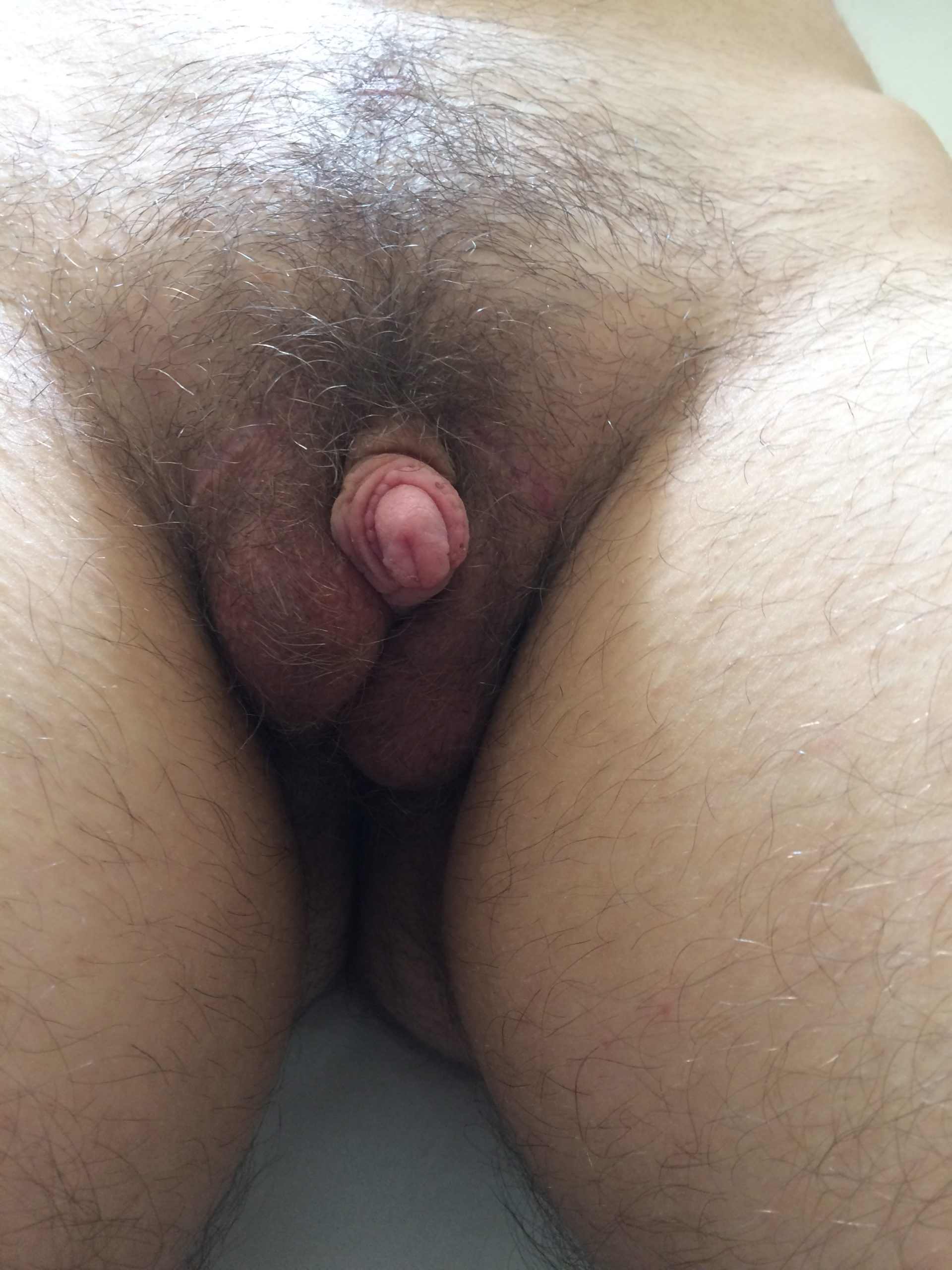



CASE 9
Outcome after surgery; voiding while standing (home video)
CASE 10
Full metoidioplasty. Outcome 6 months after surgery.

CASE 11
Metoidioplasty with preserved vagina – outcome after surgery.

1. Stojanovic B, Djordjevic ML. UPDATES ON METOIDIOPLASTY. Neurourol Urodyn. 2022 Nov 20. doi: 10.1002/nau.25102.
2. Stojanovic B, Bencic M, Bizic M, Djordjevic ML. METOIDIOPLASTY IN GENDER AFFIRMATION: A REVIEW. Indian J Plast Surg. 2022. epub 24 June 2022
3. Bordas N, Stojanovic BZ, Bizic MR, Szanto A, Djordjevic ML. METOIDIOPLASTY: SURGICAL OPTIONS AND OUTCOMES IN 813 CASES. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021; 12: 760284.
4. Stojanovic B, Bizic M, Djordjevic ML. SURGICAL ANATOMY: METOIDIOPLASTY. In: Nikolavsky, Blakely (Eds). UROLOGICAL CARE FOR THE TRANSGENDER PATIENT. 2021; pp 115-126. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG.
5. Bizic M, Stojanovic B, Bencic M, Bordas N, Djordjevic ML. METOIDIOPLASTY AS A ONE-STAGE PHALLIC RECONSTRUCTION IN TRANSMEN. Plast Aesthet Res 2020;7:43.
6. Bizic M, Stojanovic B, Bencic M, Bordás N, Djordjevic M. OVERVIEW ON METOIDIOPLASTY: VARIANTS OF THE TECHNIQUE. Int J Impot Res. 2020 Aug 21.
7. Stojanovic B, Bizic M, Djordjevic ML. URETHRAL RECONSTRUCTION IN FEMALE TO MALE GENDER AFFIRMING SURGERY. In: Martins F, Kulkarni S, Tobias R, (Eds). TEXTBOOK OF MALE GENITOURETHRAL RECONSTRUCTION. 2020; pp 883-896. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG.
8. Bizic M, Stojanovic B, Joksic I, Djordjevic ML. METOIDIOPLASTY. Urol Clin N Am. 2019; 46:555-566.
9. Djordjevic ML, Stojanovic B, Bizic M. METOIDIOPLASTY: TECHNIQUES AND OUTCOMES. Transl Androl Urol. 2019;8(3):248-253.
10. Djordjevic ML. NOVEL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES IN FEMALE TO MALE GENDER CONFIRMING SURGERY. Transl Androl Urol 2018;7(4):628-638.
11. Bizic MR, Stojanovic B, Djordjevic ML. Genital reconstruction for the transgendered individual. J Pediatr Urol 2017;13:446-52.
12. Stojanovic B, Bizic M, Bencic M, Kojovic V, Majstorovic M, Jeftovic M, Stanojevic D, Djordjevic ML. One-Stage Gender-Confirmation Surgery as a Viable Surgical Procedure for Female-to-Male Transsexuals. J Sex Med 2017;14:741-6.
13. Stojanovic B, Djordjevic M. Anatomy of the clitoris and its impact on neophalloplasty (metoidioplasty) in female transgenfers. Clin Anat. 2015; 28(3):368-75.
14. Djordjevic ML, Salgado CJ, Bizic M, Kuehhas FE. Gender dysphoria: the role of sex reassignment surgery. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:645109.
15. Djordjevic ML, Bizic MR. Comparison of two different methods for urethral lengthening in female to male (metoidioplasty) surgery. J Sex Med. 2013 May;10(5):1431-8.
16. Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Kojovic V, Stanojevic D, Korac G, Stojanovic B, Djordjevic M, One stage metoidioplasty in female to male transgender patients: the role of genital flaps for urethral reconstruction,EurUrol, Suppl 2010; 9 (2): 107 (249)
17. Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Kojovic V, Korac G, Djordjevic M, Metoidioplasty: sex reassignment surgery in female transsexuals, 21st Video Urology Congress, Egypt, 2010, p20, (II-9)
18. Djordjevic ML, Bizic M, Stanojevic D, Bumbasirevic M, Kojovic V, Majstorovic M, Acimovic M, Pandey S, Perovic S. Urethral lengthening in metoidioplasty (female to male sex reassignment surgery) by combined buccal mucosa graft and labia minora flap. Urology, 2009 Aug;74(2):349-53
19. Djordjevic ML, Stanojevic D, Bizic M, Kojovic V, Majstorovic M, Vujovic S, Milosevic A, Korac G, Perovic SV. Metoidioplasty as a single stage sex reassignment surgery in female transsexuals: Belgrade Experience. J Sex Med., 2009, 6(5):1306-1313.
20. Djordjevic M, Stanojevic D, Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Kojovic V, Martins F, Pandey S. Metoidioplasty as a one-stage gender reassignment surgery in female-to-male transsexuals. Urology, 2009;74(4, suppl 1) S164
21. Kojovic V, Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Kojic S, Stanojevic D, Korac G, Djordjevic M. Combined total phalloplasty and metoidioplasty as a single stage procedure in female to male gender reassignment surgery. EurUrolSuppl, 2009;8(8):648
22. Kojovic V, Djordjevic M, Stanojevic D, Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Pandey S. Single stage metoidioplasty (female to male surgery): the role of genital flaps for urethral reconstruction. Urology, 2009;74(4, suppl 1) S37
23. Vujovic S, Popovic S, Sbutega-Milosevic G, Djordjevic M, Gooren L. Transsexualism in Serbia: a twenty-year follow-up study. J Sex Med., 2009, 6(4):1018-1023.
24. Djordjevic M, Stanojevic D, Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Kojovic V, Pandey S, The purpose of genital flaps in urethral reconstruction in single stage metoidioplasty, 19th World Congress for Sexual Health, Goeteborg, Sweden,2009, p195-196 (PO- 1332)
25. Djordevic M, Stanojevic D, Bizic M, Majstorovic M, Kojovic V. Metoidioplasty: sex reassignment surgery in female transsexuals. J Sex Med 2008;1-149:80
26. Djordjevic M, Perovic S, Reed H. Combined buccal mucosa graft and local flap for urethral reconstruction in female transsexuals. J Urol, 2007; 177(4): 59 (abs. 175)
27. Djordjevic M, Perovic S, Korac G, Bizic M, Majstorovic M. Buccal mucosa graft combined with genital flaps for urethral lengthening in female transsexuals. Urology, 2007; 70(suppl. 3a):166(abs.MP22.01)
28. Perovic S, Djordjevic M. Metoidioplasty: a variant of phalloplasty in female transsexuals. J Urol, 2001; (suppl. 5): 165